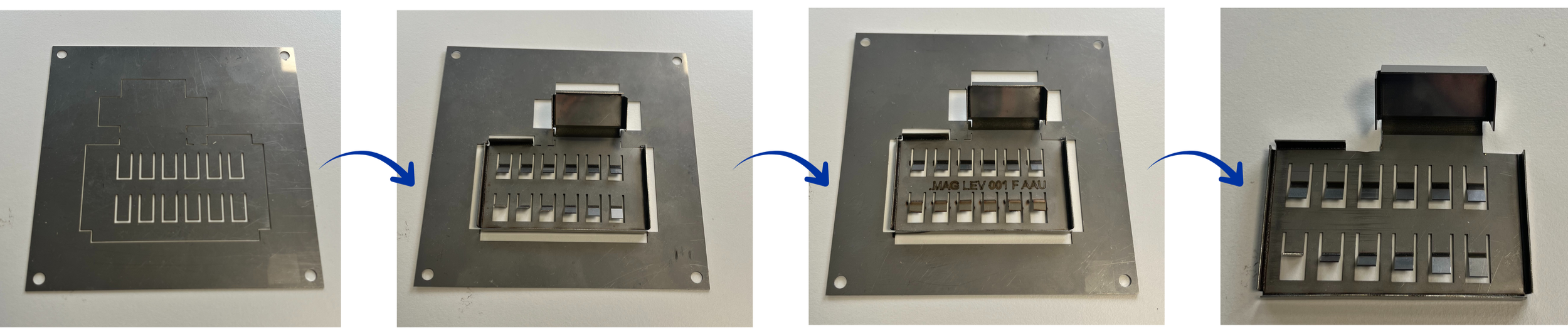
Cutting
3 Processes - 1 Machine
Forming
Engraving
Final part
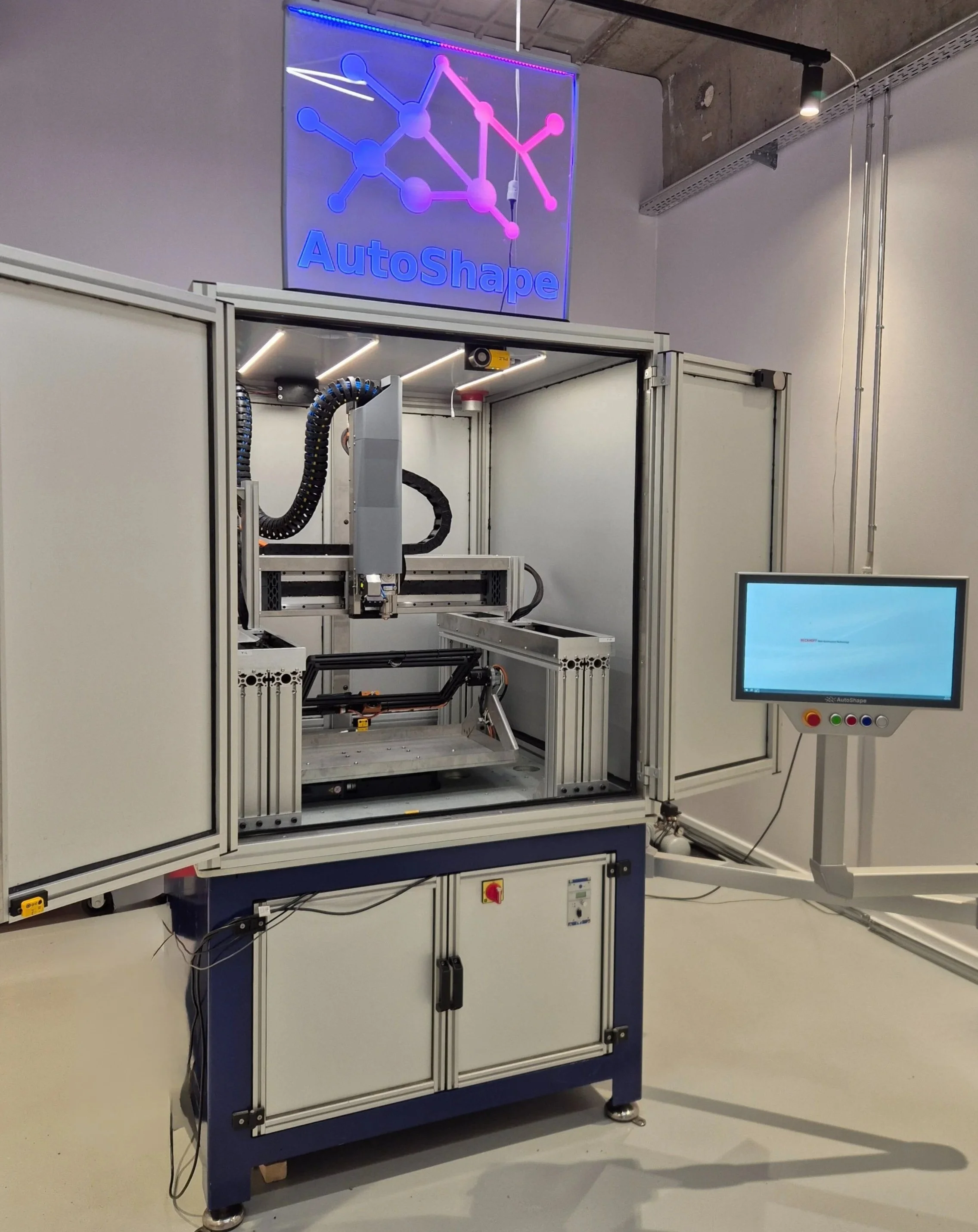
CFE-350 Machine: usability, features & capabilities
The CFE-350 is a compact Laser Integrated Manufacturing (LIM) system that combines laser cutting, laser forming, laser engraving, and integrated laser-based quality monitoring and control in one standalone machine.
It is designed for high-precision manufacturing if micro and small sheet-metal parts, produced on sheet up to 350x200 mm (with larger formats planned in future versions).
The CFE-350 runs directly from a 3D CAD model, enabling digital workflow from design to finished part with minimal setup and no dedicated tooling.
Supported materials (validated to date) include stainless steel, carbon steel, spring steel, aluminium, titanium, brass, and nickel silver. The current working thickness range is 0.1 mm foil up to 1.0 mm sheet, depending on material and geometry, with increased thickness capability planned for future generations.
-
Laser cutting · Laser forming · Laser engraving · Integrated laser-based quality monitoring
-
High-precision manufacturing of micro and small sheet-metal components
-
350 × 200 mm
(larger formats planned in future versions)
-
Stainless steel · Carbon steel · Spring steel · Aluminium · Titanium · Brass · Nickel silver
-
0.1 mm foil up to 1.0 mm sheet
(material-dependent, expandable in future versions)
-
Direct digital manufacturing from 3D CAD files
Tool-free, automated production
-
Standalone Laser Integrated Manufacturing (LIM) system
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a highly flexible, free form cutting process that gives designers and engineers exceptional freedom in part design. Complex contours, fine details, and intricate geometries can be cut with high accuracy, enabling innovative designs that are difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional cutting methods. The process creates a very narrow kerf and introduces only minimal thermal impact to the surrounding material. This preserves material properties and makes laser cutting ideal for thin sheet metal and precision components where tight tolerances and clean edges are critical.
Laser cutting works by directing a focused laser beam onto the material surface, where it locally melts or vaporises the material. A cutting gas is used to eject the molten material from the cut, resulting in clean, precise edges. In certain applications, material removal can also occur through controlled ablation.
As a non-contact, digitally controlled process, laser cutting is well suited for automated production environments and seamless integration into modern, data-driven manufacturing workflows.
Laser Forming
Laser forming is a digitally controlled, laser-driven process used to bend and shape metal without physical contact or mechanical tooling. By precisely controlling laser parameters, the desired bend angle and radius can be generated directly from digital data, enabling highly flexible and repeatable forming operations. Because no dedicated tooling is required, laser forming makes it possible to create geometries and features that are difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional press-brake bending. This eliminates tooling costs, reduces setup time, and allows rapid design iteration giving engineers and designers new freedom to develop innovative products in a cost-efficient way.
Laser forming works by locally heating a thin layer of the metal to a temperature below the melting point, causing controlled thermal expansion. By applying this heating in carefully defined patterns and sequences, the material undergoes predictable plastic deformation, resulting in precise, permanent shape changes.
As a fully digital and non-contact process, laser forming is well suited for automation and integration into modern, data-driven manufacturing environments.
Laser Engraving
Laser engraving enables permanent marking of parts with product numbers, serial numbers, IDs, QR codes, and other traceability features essential for modern manufacturing. These markings support product identification, quality assurance, and be useful for full lifecycle tracking. Beyond identification, laser engraving can be used to create functional and informational markings such as diagrams, instruction text, symbols, and graphics directly on the component. By controlling laser parameters, different contrast levels and tones can be achieved, making it possible to engrave images, logos, and even detailed artwork with high precision.
Laser engraving works by using a focused laser beam to permanently and precisely modify the surface of the material. The process is non-contact, highly repeatable, and requires no consumables, making it ideal for automated production environments and digital industry workflows.